This group has actively participated in R&D projects funded by European Union and the government of Spain. Our contribution has mainly concentrated or robotic and computer vision. Following is the summary of the projects we were/are involved.
IRAS-HUB
Link: IRAS-HUB Website
Abstract: The project Capacity Building in Robotics & Autonomous Systems in India (IRAS- HUB) aims to establish three hubs in Robotics and Autonomous Systems (RAS) in India to overcome the sparsity of skilled talent in robotics technology. The Hubs will be equipped with prototyping equipment and robotics software and will train researchers from Indian Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in RAS with experts from EU HEIs.
Project Number
101083029-ERASMUS-EDU-2022-CBHE-STR
Funding
Erasmus+ Capacity Building for Higher Education-Strand 2
Duration
1/3/2023-28/2/2026
Partnership
1. IIIT-DELHI Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology Delhi – India (Coordinator)
2. IIIT H International Institute of Information Technology Hyderabad – India
3. IIIT A Indian Institute of Information Technology Allahabad – India
4. UNIGE Universita Degli Studi Di Genova – Italy
5. WUT Politechnika Warszawska – Poland
6. URV Universitat Rovira I Virgili – Spain
7. CRE.THI.DEV Dimiourgiki Skepsi Anaptyxis -Greece
8. GGSIU Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University – India
9. ADDVERB TECHNOLOGIES Addverb Technologies Limited- India
10. TUC Technical University of Crete/Polytechneio Kritis – Greece
Target Horizon
Link: Target Horizon
Abstract: Introducing virtual twin-driven AI models for atrial fibrillation (AF) and its complications such as AF-related stroke (AFRS). Novel personalised virtual twins and decision-support tools to help prevent AF and AFRS, while optimising acute management and rehabilitation. Ultimately, the goal is to provide a better quality of life for patients and caregivers, and lower healthcare costs. With AF being a widespread irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia), it significantly increases the risk of complications such as stroke and heart failure. TARGET represents a significant milestone by reshaping risk prediction, diagnosis, and management of AF and AFRS, and accelerating the translation of research into practical applications.
Retina Read Risk
Link: Retina Read Risk
Abstract:This project aims to improve early detection of diabetic retinopathy (DR), a microvascular complication of type 1 and type 2 diabetes affecting the retinal blood vessels. Early detection is crucial, as DR can lead to vision loss. Despite being asymptomatic in its early stages, it affects a significant portion of diabetes patients. The project focuses on utilizing telemedicine and specialized cameras to overcome inefficiencies in healthcare systems and expand access to screening, particularly in rural and underserved areas. This approach has the potential to reduce preventable blindness and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.

BosomShield
Link: BosomShield
Abstract:BosomShield proposes to join the two disciplines (pathological and radiological imaging) in a software that will analyse these images to classify the breast cancer subtypes and predict (together with the complete clinical history of the patient) the probability of relapse for distant metastasis. In addition, BosomShield will provide high-level training in breast cancer research to young researchers by offering the necessary transferable skills for thriving careers underpinned using diverse disciplines, digital radiology and pathology, biomedical, AI, privacy and software development.

RadioCancers
Abstract: Robust radiomic features with clinical data modelling for characterizing common cancers aggressiveness and prognosis through computer analysis of multimodal radiological images. Program: National Program of Information Technology. Funding body: Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness. Project / ref.: PID2019-105789RB-I00. Duration, from: 2020 to: 2023
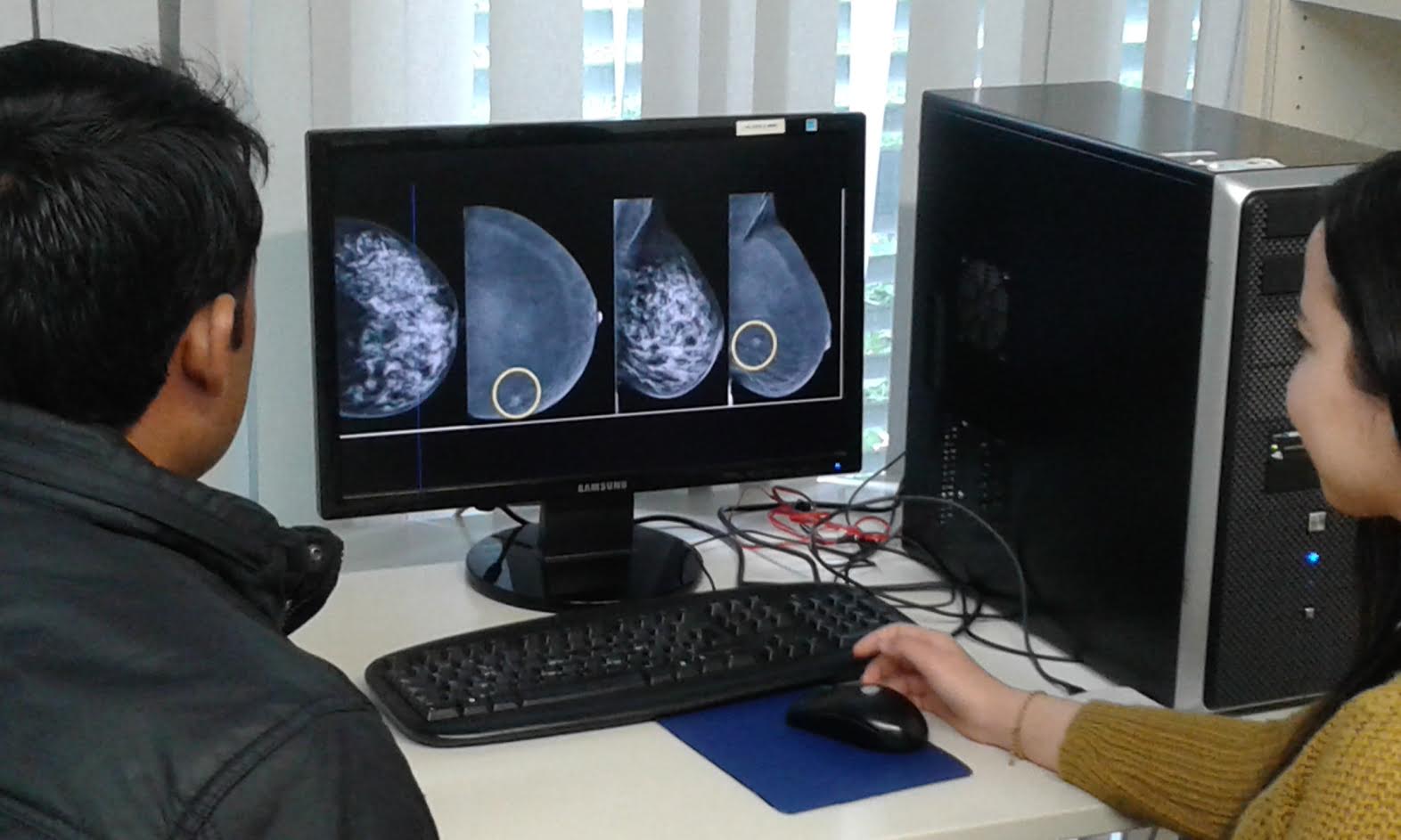
P-BreasTreat: Personalized treatment of breast cancer by determination of the molecular
Abstract:There is an unstoppable tendency towards personalized medicine in order to achieve both, diagnosis and treatment, and monitoring more effective for each patient. In this line, we propose the P-BreasTreat project, aimed at the personalized treatment of breast cancer by developing new computational techniques for image and data analysis. The ultimate purpose is to improve the effectiveness of current methods for determining the level of malignancy associated with that cancer tumors and also to propose models to prevent relapse and improve the quality of life of the patients.
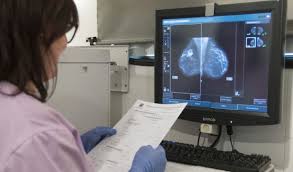
IA-BIOBREAST: Pixel-level analysis of texture features and fusion of multimodal information
Abstract:Detection based on screening programs in high-risk populations is a major asset in the struggle against Breast Cancer. Currently, screening programs in most developed countries focus in analysing digital mammography images. Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) systems provide decisive help in this task. Nevertheless, latest tendencies imply that not all women should follow the same screening protocol (i.e. systematic mammography every two years), but they should be stratified according to several criteria. This criteria stand mainly for cancer risk biomarkers such as breast density or previous lesion evolution. The capacity to stratify patients improves diagnostic efficiency by using different medical imaging modalities. Specifically, personalised screening programs make use of the image modality that provide the better information for each patient type.
BEAGLE
Link: BEAGLE
Abstract: This project aims to demonstrate the improvement of productivity and efficiency in the processes of knowledge valorization and value creation in the link between academia and industry. Specifically, it focuses on increasing collaboration between universities and research centers, on one hand, and industry, on the other, to build a community in different countries and industrial sectors of Europe that identify new market niches and new sustainable ways of creating value.
Cuidem el que ens uneix. Carreteres més segures i sostenibles
Link: Cuidem el que ens uneix
Abstract:This operation will develop the architecture necessary to fulfill the objectives of the previous operation. Specifically, a cloud services platform will be developed where massive data processing (Big Data) will be carried out with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and a mobile application that will allow users to report incidents in real time, either in the form of text or images.

Hybrid Robot UGV/UAV Ultra-High Mobility
Abstract:This project aims at designing a new concept of mobile hybrid robot UGV-UAV (Unmanned Ground Vehicle – Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) that allows for substantially increasing the degree of mobility in today’s robots. Soil properties impose severe restrictions on the mobility of robots (mobility in the broadest sense refers to the performance of the robot in relation to the field, ability to negotiate obstacles and avoid them, ability to overcome rough terrain and crossing streams.)
The combination of two locomotion systems in a single hybrid system will allow the speed, controllability and autonomy of a land mobile platform, adding the mobility of a system capable of flying. The project aims to develop the associated technologies (stability control, attendance control, software and control architectures, HRI interfaces, navigation systems and assistance through Artificial Vision) to develop a new type of robot to be applied in multiple scenarios.
3D Scene Interpretation Through Computer Vision from the Coordinated Analysis of Images Obtained by team of mobile robots
Abstract:This project aims at designing new computer vision techniques that allow the automatic interpretation of 3D scenes from the analysis of images provided by a team of mobile robots. The new schemes will take advantage of the different images corresponding to a same region delivered by each member of the team by means of a coordinated inspection. Such a interpretation is expected to contribute to increasing the performance of cooperative tasks developed by the team of robots. In this way, the accuracy of both the self-localization of mobile robots in the space and the global 3D model of the environment is desired as a result of those techniques.
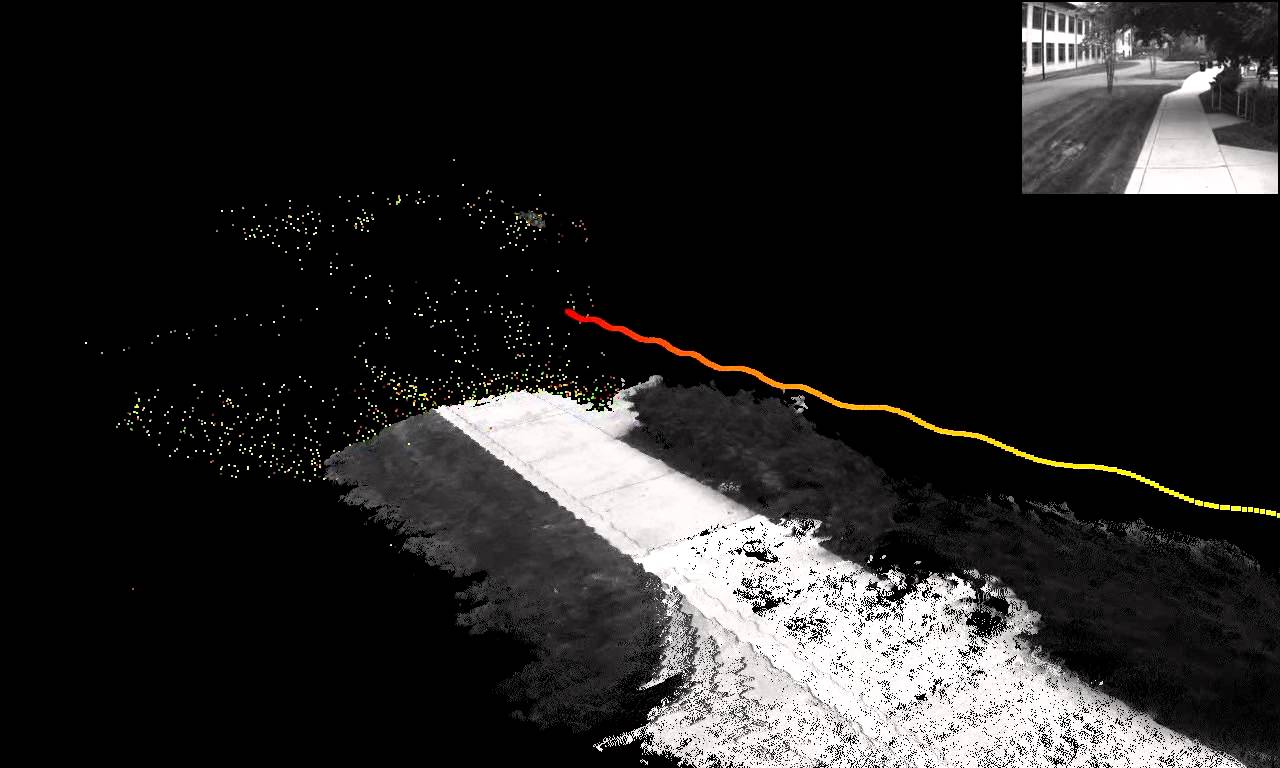
Coordinated Exploration of Wide-Area Environments with Multiple Robots Through Vision-Based 3D SLAM
Abstract:This project aims at designing and implementing new exploration strategies that allow a team of mobile robots to deploy collaboratively in order to obtain processable three-dimensional models of wide-area, unknown environments. Every robot will map its surroundings and simultaneously determine its position and orientation in space by processing visual information obtained by means of an off-the-shelf stereo camera. The accuracy of both the robot’s pose and the locally obtained 3D models will be continuously improved by integrating information gathered by separate robots. In this way, a consistent global 3D model of the environment is expected as a result of the exploration process.
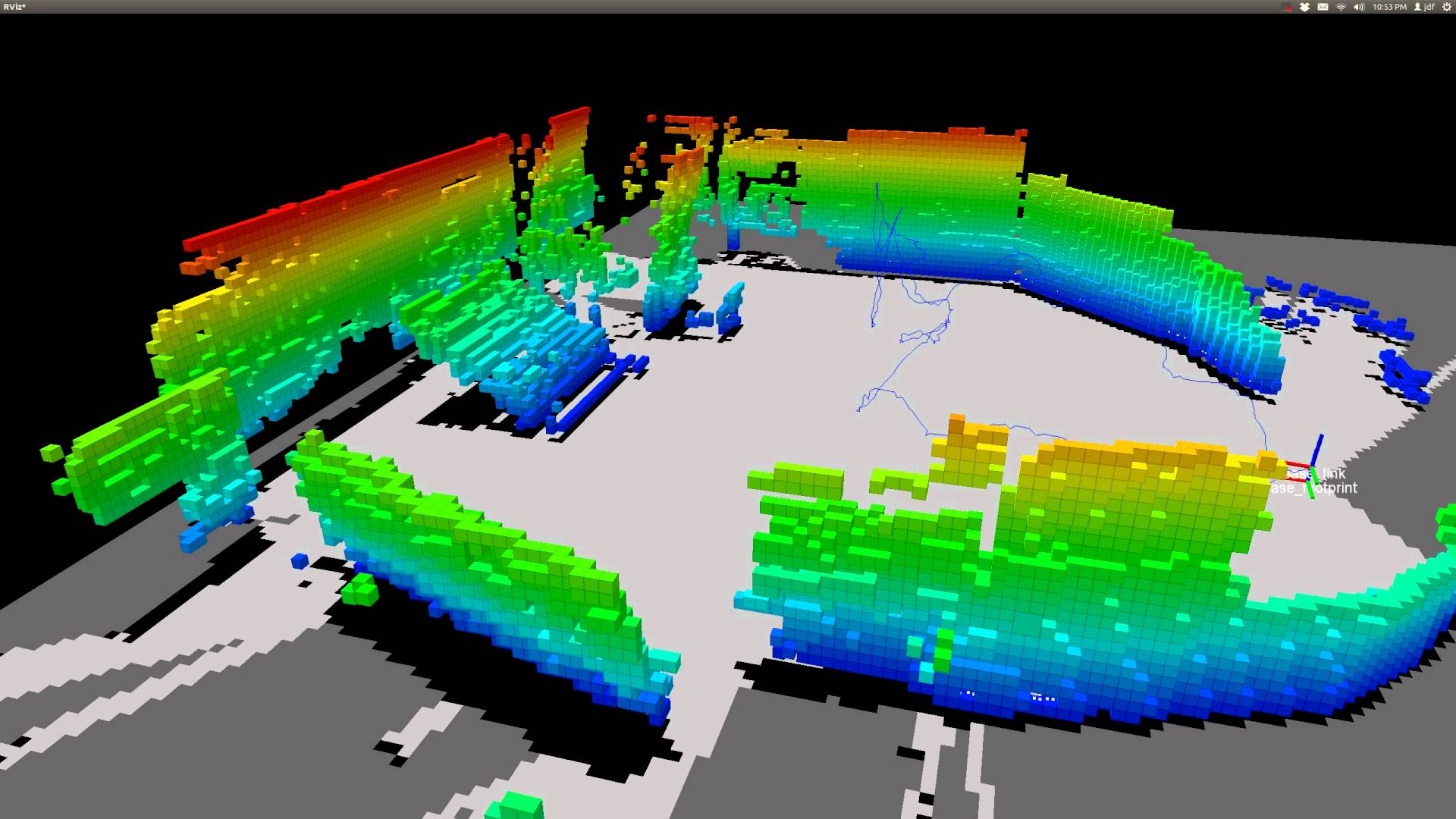
Multiagent System of Advanced Observers for Scene Analysis and Recognition in Adverse Environments
Abstract:This project aims at designing and implementing a computer system based on multiagent technology that allows the coordination of a team of mobile robots endowed with sensory devices, in order that they deploy over an unstructured and possibly adverse environment, and cooperate for obtaining information about it. Information acquired in a distributed manner by the robotic team must be analyzed and integrated with the purpose of obtaining a complete and precise computer model of the recognized area. That model will simplify further both planning and decision making activities performed by other agents in charge of the execution of more complex tasks related to the aforementioned environment (rescue personnel, fire brigades, etc.). Hence, the goals of this project are similar to those of the Robocup Rescue Robot League, although we do not pretend to participate in the tournament.
AbleGames: Gamification for a better life.
Link: AbleGames
Abstract:Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a frequent neurological disorder (2 per 1k births). The EU has 0.7m of 17m persons with CP globally. Therapy can cost €45k/year – a huge burden on families. Playing digital games, as Europe 2020 identifies, can promote health & well-being for people with such disabilities. AbleGames will be a disruptively innovative social-collaboration serious gaming platform to personalise & improve the physical therapy, peer community inclusion, quality of life & enjoyment of people with CP. There are many game platforms (e.g. Steam, Origin, Epic), but none for, or usable by, people with CP. Our platform will constantly adapt multiplayer top-quality games to each individual’s abilities to foster rehabilitation progress & social collaboration using AI technologies. The players will interact with non-immersive virtual reality scenarios using balance sensors & smart low-cost vision systems based on machine learning models.

GABLE: Gamification for Better Life
Link: GABLE
Abstract:The main objective of the GABLE project is to launch a social platform for personalized games that would dramatically enhance the living conditions of people with Cerebral Palsy (CP). This platform continues the work previously done in the “Game-abling” project, and updates it to relevant emerging gaming technologies, such as augmented reality, while, at the same time, introducing machine learning in the backbone of the platform, in order to provide the level of personalization envisioned. As such, carers for people with CP will have the tools to personalize the games. Besides, it offers control mechanisms that allow the carers to adequately monitor the progress of the patients. The focus of the games in this platform is on social inclusion, by means of improving the physical activity of CP patients, through the use of multiplayer technologies in the creation of such games, which will facilitate the development of relationships within groups of CP patients, as well as outside these groups.

Rehabibotics: Using Humanoid Robots to Convey Rehabilitation Therapies to Disabled People
Abstract:Analysis of requirements for an efficient cognitive stimulation using humanoid roots, among individuals with Intellectual Disability(ID), as well as learning of engagement/emotional state during HRI among individuals with ID using physiological signals and external cues and adaptation of robot behavior for an effective cognitive stimulation, using knowledge of actual emotional and engagement state of participants.
Game-abling: Platform of Games for People with Cerebral Palsy to Enhance Living Adjusment
Abstract:Cerebral Palsy (CP) is one of the most frequently conditions in childhood, with an incidence of 2 per 1,000 live births. In the EU there is 1.3 out of 15 million persons with CP in the world. This neurological disorder affects body movement, balance and posture and almost always is accompanied by other cognitive or sensory impairments like mental retardation, deafness and vision problems. The severity of these problems varies widely, from very mild and subtle to very profound.



